
The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, act as legal, financial or credit advice. See Lexington Law’s editorial disclosure for more information.
Taking out a debt consolidation loan may trigger a hard credit check, which could cause your credit score to temporarily drop by a few points. However, as you make payments on time and in full, you’ll likely see your credit score increase.
Juggling multiple types of debt means you have to keep track of multiple payments each month. Missing even one of those payments can cause your credit score to drop. Using debt consolidation loans can help you roll multiple debts into a single loan, making it easier to keep track of what’s due and when. But do debt consolidation loans hurt your credit?
As with any new loan, debt consolidation loans can cause your credit score to drop temporarily. But that doesn’t mean they’re not a helpful method to pay off your debt.
Let’s take a look at how debt consolidation loans work, how you can use them to repay what you owe and how to tell if these loans are a good fit for your financial situation.
In this post:
- What is debt consolidation, and how does it work?
- Types of debt consolidation
- How debt consolidation impacts your credit
- Alternatives to debt consolidation
- Is debt consolidation a good idea?
- Debt consolidation FAQ
What is debt consolidation, and how does it work?
Debt consolidation is a method of combining multiple outstanding debts into a single line of credit. For example, you can consolidate multiple credit cards or a mix of credit, such as a mortgage, a vehicle loan and medical bills, into a single new loan. Debt consolidation not only organizes your debt into a single payment but can also offer a smaller interest rate.
Debt consolidation may be a good choice if:
- You’re struggling to keep track of multiple due dates
- Interest rates have dropped since you took out your original debt
But if you have a small amount of total debt or only have one or two loans or lines of credit to your name, debt consolidation may not be beneficial for your financial situation.

Types of debt consolidation
There are several debt consolidation methods to choose from. Each one carries its own benefits and risks, making it important to educate yourself on potential impacts. Here are some of the most commonly used debt consolidation options you may want to consider:
- Balance transfer cards: A balance transfer card allows you to roll several debts into a single credit card, ideally with a lower interest rate. Many of these cards offer a promotional period with zero percent interest but require good to excellent credit to qualify.
- Personal loans: These loans give you a lump sum amount that you can use to pay off multiple lines of credit or loans. Most personal loans come with fixed interest rates, so you won’t have to worry about payments changing unexpectedly.
- Your 401(k) account: Traditional 401(k) accounts let you borrow up to half of your vested balance or up to $50,000, whichever is smaller. Before you decide if you should borrow from your 401(k), consider how doing so may impact your retirement. You may lose out on money you would’ve made if the funds had remained in the account.
- Home equity loans and lines of credit: If you’re a homeowner, you may be able to use a home equity loan or line of credit to pay off your debt. Home equity loans function like personal loans, while home equity lines of credit (HELOCs) work like a credit card. Both options require using your home as collateral. This means failing to repay the debt can result in losing your home.
Ultimately, the best debt consolidation option depends on your credit score and amount of debt. If you need to pay off larger amounts of debt, using personal loans, HELOCs or home equity loans may be a good choice. But if you’re trying to consolidate several credit card balances, a balance transfer could save you money in the long run.
How debt consolidation impacts your credit
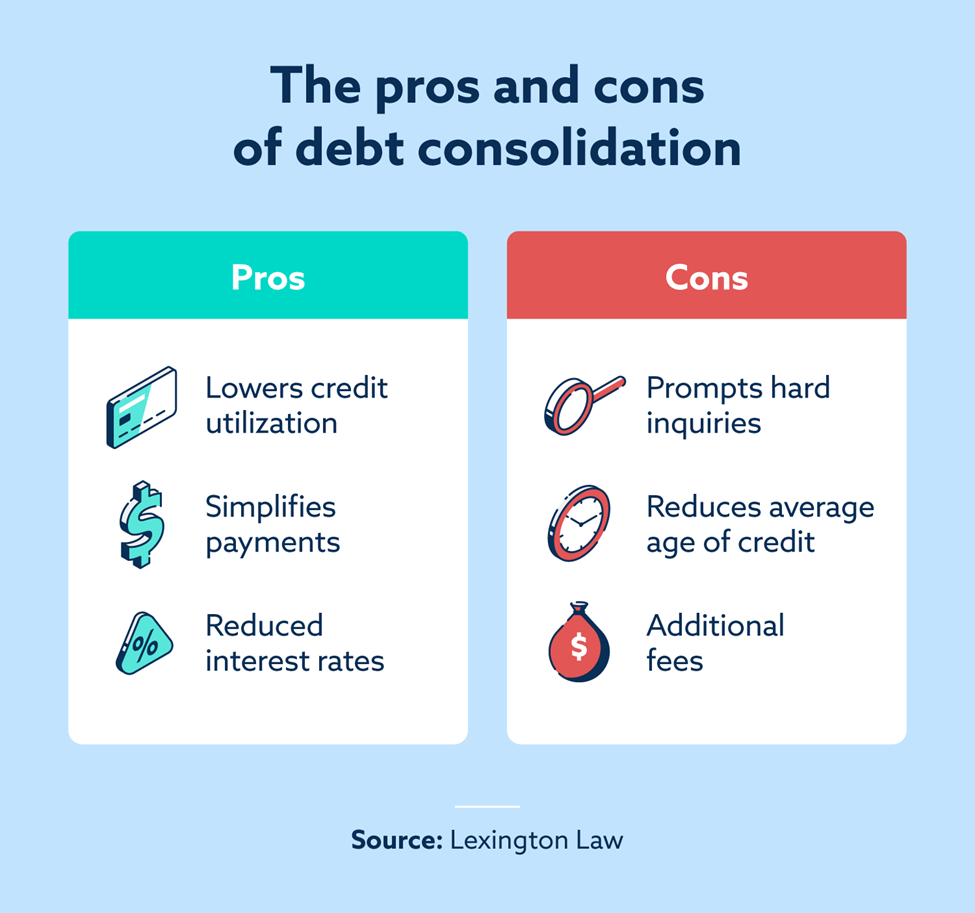
Exploring the pros and cons of debt consolidation can help determine if it’s the appropriate financial strategy for your situation.
Benefits of debt consolidation
Debt consolidation can help you:
- Build a history of on-time payments: Making on-time payments carries the biggest weight in calculating your credit score. If you consistently meet payment due dates, your score can increase.
- Lower credit utilization: Credit utilization, or the amount of credit owed, accounts for thirty percent of your FICO® score. Debt consolidation may help increase the amount of available credit, which can improve your score if you don’t acquire any new debt.
- Access lower interest rates: Depending on your credit score, you may qualify for a lower interest rate when consolidating debt. This can help you pay off debt faster, reducing the amount you owe and boosting your score.
- Diversify credit mix: The types of credit used also impact your score. For example, if credit cards are your only lines of credit, taking out a personal loan to consolidate debt diversifies your credit mix, improving your score.
Drawbacks of debt consolidation
Conversely, debt consolidation may result in:
- Higher interest rates: If you have poor credit, you may not qualify for a lower interest rate than your existing debts.
- Extended loan terms: While monthly payments might be lower, a longer repayment term could result in paying more in total interest over time.
- New fees: Debt consolidation loans may involve origination fees, balance transfer fees or closing costs. These upfront charges can reduce the loan’s financial benefits.
- Credit inquiries: Applying for a consolidation loan results in a hard inquiry on your credit report, which can temporarily lower your credit score.
- Closed accounts: If you close credit card accounts after consolidating, your credit utilization ratio might increase, which can negatively affect your credit score.
| The pros and cons of debt consolidation | |
| Pros | Cons |
| Builds a history of on-time payments Lowers your credit utilization ratio Helps you access lower interest rates Diversifies your credit mix | Requires a hard credit check Charges origination fees, balance transfer fees or other closing costs Extends your loan’s terms Closes old accounts, which may shorten average credit age |
Alternatives to debt consolidation
If debt consolidation doesn’t work for your situation, that’s okay. Other debt management methods may provide needed relief. Let’s take a look at some alternative debt relief options you may want to consider:
- Debt management programs: Debt management programs connect you with a counselor who negotiates with creditors on your behalf to score more favorable terms, such as lower interest rates.
- Debt settlements: In debt settlements, you negotiate directly with creditors to reduce your monthly payments or interest rates. This may help you repay what you owe faster.
- Bankruptcy: Bankruptcy can help when you’re overwhelmed by debt. Chapter 7 clears most debts quickly, while Chapter 13 sets up a 3 – 5 year repayment plan to help you catch up. Both offer powerful tools for a fresh start. It’s best to consult with a bankruptcy attorney to find the right option for your situation.
- The debt avalanche repayment method: The debt avalanche repayment method encourages you to pay more than the minimum payment on the highest-interest debt first until it’s paid off. You then repeat the process with the next highest-interest debt until your debts are repaid in full.
Is debt consolidation a good idea?
Debt consolidation options like personal loans and balance transfers may hurt your credit temporarily, but they can help you boost your score in the long run.
Consulting with a financial advisor may give you insight into how each option will impact your financial situation. But you’ll still want to know where your credit currently stands before you make your decision.
Take our free credit assessment to see your FICO score and a short summary of your credit report.
Debt consolidation FAQ
Does consolidating debt affect my credit?
Consolidating your debt can impact your credit score in two ways. First, you may see a temporary drop in your credit score when the lender runs a hard credit inquiry for your debt consolidation loan.
Second, you may see your credit score improve as you pay off your old debts and start making payments on your debt consolidation loan. As long as you make those payments on time and in full, you’ll stay in good standing.
How long does debt consolidation stay on your credit report?
Debt consolidation doesn’t show up on your credit report, but any debt consolidation loans you take out will show up as new loans. Those loans will stay on your credit report while you’re making payments and may show up on your report for up to 10 years after you pay them off in full.
How can I consolidate credit card debt without hurting your credit?
Consolidating your debt may cause a temporary drop in your credit score, whether you’re applying for a balance transfer credit card or a debt consolidation loan. But you may be able to minimize the impact by:
- Leaving your old credit cards open after paying them off.
- Paying off your balance transfer or debt consolidation loan quickly.
- Making on-time payments on debt consolidation loans each month.
- Limiting the number of new credit cards or loans you apply for.
Note: Articles have only been reviewed by the indicated attorney, not written by them. The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, act as legal, financial or credit advice; instead, it is for general informational purposes only. Use of, and access to, this website or any of the links or resources contained within the site do not create an attorney-client or fiduciary relationship between the reader, user, or browser and website owner, authors, reviewers, contributors, contributing firms, or their respective agents or employers.
